Last updated on July 14th, 2024 at 05:49 pm
The Living world cbse class 11 biology notes. This cbse biology class 11 notes is having brief explanation of every topic that NCERT biology syllabus has.
You will also get ncert biology class 11 pdf, ncert solutions, cbse class 11 biology sample paper, cbse biology class 11 previous year paper.
What Is Living?
A living thing pertains to any organism that possesses the characteristics of life or being alive. The earth serves as a home for living organisms. It lives in both land and water.
These living organisms have different characteristics such as organized structure, requiring energy, responding to stimuli and adapting to environmental changes, and capable of reproduction, growth, movement, metabolism, and death.
Every living organism has a definite life span of birth, growth, maturity and death.
Some of the important characteristics of living organisms are given below:
Growth
Living organisms grow by cell division. A single cell divides into various cells and becomes tissue, further tissue divides and makes organisms.
Plants grow continuously throughout life in their meristematic area but animals grow till a certain age. Living Organisms grow internally due to addition of materials and formation of cells inside the body.
However, certain body parts like nails, hair and replacement of lost cells continue throughout life. In unicellular organisms, growth can be observed under the microscope.
Reproduction
It is the formation of new living organisms of the similar kind. Reproduction is not essential but required for perpetuation of the population.
In sexual reproduction two parents are involved to produce similar kinds of individuals. In asexual reproduction single parent is involved and reproduction occurs by fission, fermentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation etc. In unicellular organisms, growth and reproduction are synonyms.
Some organisms don’t reproduce like mules, sterile worker bees, infertile human couples etc.
Metabolism
Metabolism is the process by which your body converts what you eat and drink into energy. During this complex process, calories in food and beverages are combined with oxy
Metabolism is described as all chemical reactions which are involved in maintaining the living state of the cells and the organism.
It is closely linked to nutrition and the availability of nutrients.
Nutrition which forms energy is one of the vital components of metabolism. All kinds of activities of an organism including growth, movements, development, reproduction etc. are due to metabolism.
Metabolism can be divided into two categories:
Catabolism – the breakdown of molecules to obtain energy
Anabolism – the synthesis of all compounds needed by the cells
Difference between Anabolism and Catabolism
Anabolism
- It is the some total of constructive process
- Complex system are formed from simple ones
- Energy is stored
- Required for growth and maintenance
Catabolism
- It is the sum total of destructive possesses
- Simpler substance are formed from complex one
- Energy is released
- Required for performance of activities
Consciousness
All living organisms have the ability to sense their environment. They respond to various stimuli (physical, chemical and biological)
These stimuli are light, water, temperature, pollutants, other organisms, etc.
Humans have an additional ability of self-consciousness. They are aware of themselves.
Therefore, living organisms are self-replicating, evolving and self-regulatory interactive systems capable of responding to external stimuli.
The body of living organisms is well organized, several components and sub components cooperate with each other for the functioning of the whole body.
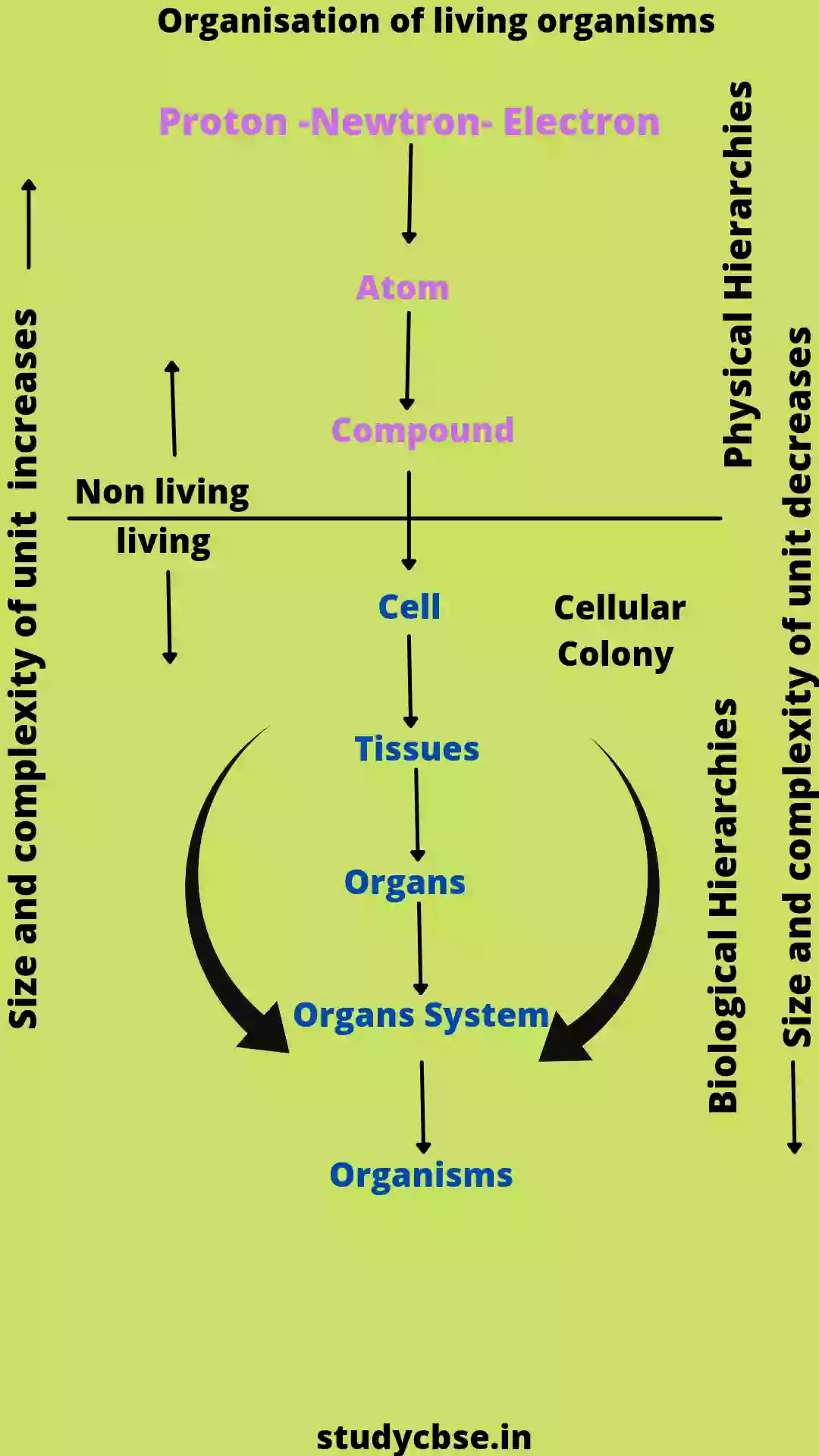

Physical and Biological Hierarchies
There is a physical (non-living) and biological hierarchy in the organization of the living body. In physical hierarchy, various non-living components form compounds, which finally enter the living world in the form of cells.
These cells organize tissues that form organs and several organs form organ-systems. Finally, many organ systems organise and form a living organism.
Living organisms have many other features that differentiate them from nonliving things, such as, shape & size, life cycle, movement, self-regulation, variations, adaptations, healing & repair, excretion and death.
Diversity In Living World – Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the total number and types of organisms found on earth. It is the occurrence of a variety of life forms which are differing in morphology, size, colour, anatomy, habitats and habits. Each different kind of plant, animal or microorganisms represents a species.
Presently there are 1.7 – 1.8 million living organisms known to science. Out of which 1.25 millions are animals and about 0.5 millions are plants.
This huge available variety cannot be studied and identified without having a proper system of classification and nomenclature.
Systematics
It refers to systematic arrangement of organisms. Systematic deals with unique properties of species and groups to recognise, describe, name and arrange the diverse organisms according to an organised plan.
Identification
It refers to finding the correct name and appropriate position of an organism. The morphological and anatomical characters are examined for proper identification.
Classification
It is not possible to study all the living organisms without their classification. It is the process by which organisms are grouped into categories based on some easily observable characters.
Biological classification is the scientific arrangement of all the organisms in a hierarchy of groups and sub-groups on the basis of similarities and differences in their traits.
Various terms used as part of the classification are as follow:
Nomenclature
It is the system of naming any living organism, so that a particular organism is known by the same name all over the world.
Living Organisms either known by their common name or scientific name.
Common name are local names given to an organism in a specific language in a particular region. There may be different names of a same organism in different regions even with in a country. e.g. Dog – kukur (bengali) kutta (hindi) nay (tamil).
Scientific name are biological name given by biologists. This name of organisms is same in every part of the world.
The scientific name has two segments – the generic name and specific epithet. This system of providing name with two components is called as Binomial Nomenclature given by Carolus Linnaeus, e.g. Homo sapiens (wise men). Here ‘Homo’ is the generic name and sapiens is the specific epithet.
The system of providing scientific names is called binomial nomenclature.
International Nomenclature Codes
- International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN)
- International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN)
- International Code of Bacteriological Nomenclature (ICBN)
- International Code of Viral Nomenclature (ICVN)
- International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP)
Rules for Nomenclature
- Each name must have two words- the genus and the specific epithet
- Should be independently underlined when written manually and should be italics when printed
- Names should be in Latin
- Generic name begins with upper case and the specific name begins with lower case
Taxonomy
It is the process of identification, classification, nomenclature and organisation of life forms considering the …
-external and internal structure (comparative morphology)
-structure of cells (cytology)
-development process (embryology) -ecological information of organisms (ecology)
Taxonomy provides the information according to similarities, dissimilarities and evolutionary relationships of various organisms.
Carolus Linnaeus is known as father of taxonomy
Taxonomic Categories
It refers the rank or level in the hierarchical arrangement in ascending order. The seven mandatory categories as listed below:
Classification is not a single step process. It involves hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a rank or category. Since, the category is a part of overall taxonomic arrangement, it is called the taxonomic category and all categories together constitute the taxonomic hierarchy.
Plant– Kingdom – Division – Class – Order – Family – Genus – Species
Animal– Kingdom- Phylum – Class – Order – Family – Genus – Species
Kingdom: It is the highest category in taxonomy. This includes all the organisms, which share a set of distinguished characters.
Phylum or Division: The term Phylum is used for animals, while division is used for plants. It consists of more than one class having some similar corelated characters.
Class Many orders related to each other are incorporated into a class.
Order includes a few related families
Family is an assembly of related genera
Genus is a gathering of related animal having similar characters
Species is basic taxonomic category, which consists of any animal group that are firmly related and resemble one another more closely than individuals of other species.
Taxonomic Aids
It refers to the techniques, stored information and procedures useful in identification and classification of entities.
? Herbarium
It is the storeroom of assembled plant samples. These samples are dried, squeezed and protected on sheets. These sheets are systematically ordered in accordance with the classification system universally accepted.
The Herbarium sheet also consists the scientific name, date, the spot of gathering, name of the collector, family and much more concerning the sample.
? Museums
It is a repository which is having an assembly of different plant and animal samples preserved for study and further information source.
Here the samples are preserved either as dry or in additive arrangements. It usually has an accumulation of skeletons of animals too.
? Zoological park
It is the place where wild animals are kept with secured conditions of nature under human care. It enable us to learn about their food habits and behaviour. Zoological parks provide natural habitat to the animals.
? Botanical Garden
Botanical garden consists of an accumulation of living plant species developed to identify and reference. Every plant has a label exhibiting its scientific name and family name. Botanists and gardeners look after plants in botanical gardens.
? Key
Key is use for identifying both plants and animals in light of similarities and dissimilarities.
Turrill classified taxonomy into three different types:
? Alpha taxonomy: It is concerned with collecting and identifying organisms based on gross morphology, field and herbarium studies helping to compile monographs and flora and also in identifying plants
? Beta taxonomy: It is concerned with collecting and identifying based on morphology and evidence from anatomy, genetics, cytology, physiology, etc.
? Omega taxonomy: It is concerned with all microscopic observations and biochemical evidence equal to new systematics based on the phonetic classification.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is living thing?
Answer: A living thing pertains to any organism that possesses the characteristics of life or being alive. The earth serves as a home for living organisms. It lives in both land and water.
Q2. What is taxonomy?
Answer: It is the process of identification, classification, nomenclature and organisation of life forms considering the …-external and internal structure (comparative morphology)
-structure of cells (cytology)
-development process (embryology) -ecological information of organisms (ecology)
Q3. What is nomenclature?
Answer: It is the system of naming any living organism, so that a particular organism is known by the same name all over the world.Living Organisms either known by their common name or scientific name.
Q4. What are the full form of ICBN, ICZN, ICBN, ICVN, ICNCP ?
Answer:
International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN)
International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN).
International Code of Bacteriological Nomenclature (ICBN).
International Code of Viral Nomenclature (ICVN).
International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP).
Click Here To Learn Class 11 Physical Education Notes
Final Words
From the above article you must have learnt about ncert cbse class 11 biology notes of chapter 1 The Living World. We hope that this crisp and latest biology class 11 notes will definitely help you in your exam.