Last updated on July 14th, 2024 at 05:08 pm
How Do Organism Reproduce Notes
Below are some of the very important NCERT Class 10 Science chapter 8 How do organism reproduce notes and Question with Answers. These Class 10 How do organisms reproduce notes and questions have been prepared by expert teachers and subject experts based on the latest syllabus and pattern of term 2. Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept.
These Questions for Class 10 Science How do organism reproduce notes and questions are very important for the latest CBSE term 2 pattern. These class 10 notes and Q and A are very important for students who want to score high in CBSE Board.
We have put together these NCERT Questions of Class 10 Science chapter 8 How do organism reproduce notes and questions with answers for practice on a regular basis to score high in exams. Refer to these Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
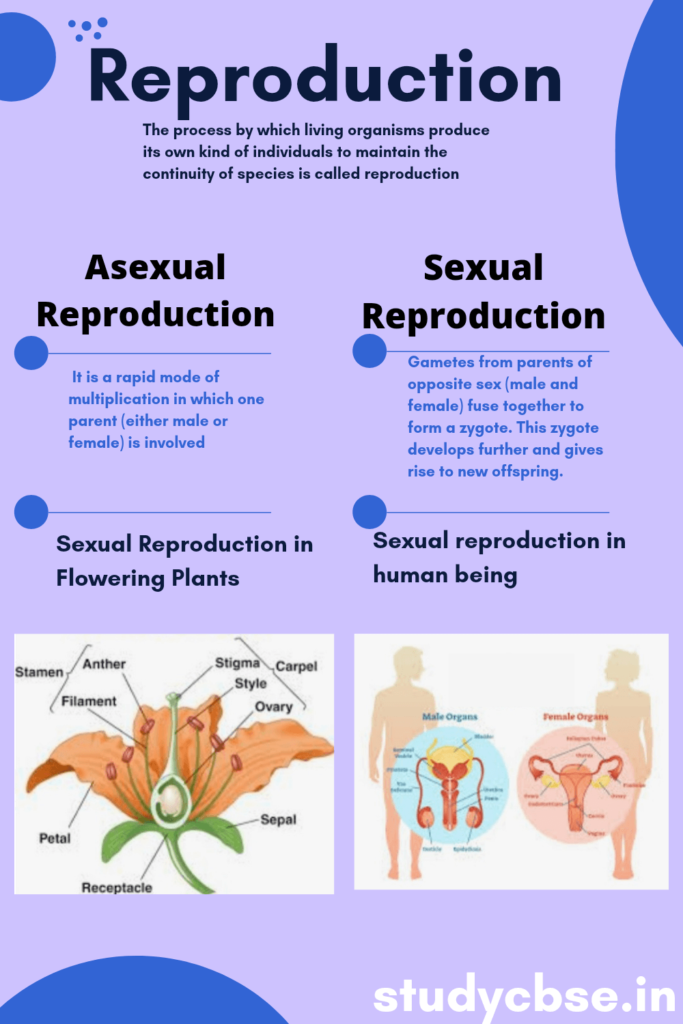
The process by which living organisms produce its own kind of individuals to maintain the continuity of species is called reproduction. Like other essential life processes, reproduction is not essential to maintain the life of an individual. But is a fundamental feature of all known life, each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction.

The Fundamentals of Reproduction
The process of reproduction involves the formation of DNA copy and other cellular apparatus required by the cells of an individual.
DNA is the blueprint of all the basic design of organisms. It is present in the nucleus of a cell as a condensed structure called chromosome.
It acts as the information source and helps in making different proteins and cellular machinery of cell, which makes up the different body designs.
Variations
DNA copying during cell division always causes some or other type of variations in newly formed cells. This brings the differences found in the morphological and physiological features of an organism.
Since no biochemical reaction is absolutely reliable, DNA copies generated are similar, but not absolutely identical. Variations lead to evolution by increasing the chances of survival of some individuals. Hence, important for
Types of Reproduction
Reproduction is mainly of two types, i.e. asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction. It is a rapid mode of multiplication in which one parent (either male or female) is involved. The new individuals produced are identical to their parents.
Sexual Reproduction. In this process, the gametes from parents of opposite sex (male and female) fuse together to fonn a zygote. This zygote develops further and gives rise to new offspring. The individual produced by this method exhibits variation.
I. Modes of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction occurs in unicellular organisms fission, budding, spore formation, fraginentation, regeneration fin animals) and vegetative propagation (in plants). It oeeurs in multicellular organisms by budding and regeneration.
These are as follows
(i) Fission. The process where a unicellular organism splits itself into two or more daughter cells. It is of two types,
(a) Binary Fission In this process, parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells, e.g. Amoeba, Leishmania.


(ii) Fragmentation The parent body on maturation breaks up into two or more small fragments, which later grow into a complete new organi e.g. Spirogyra,
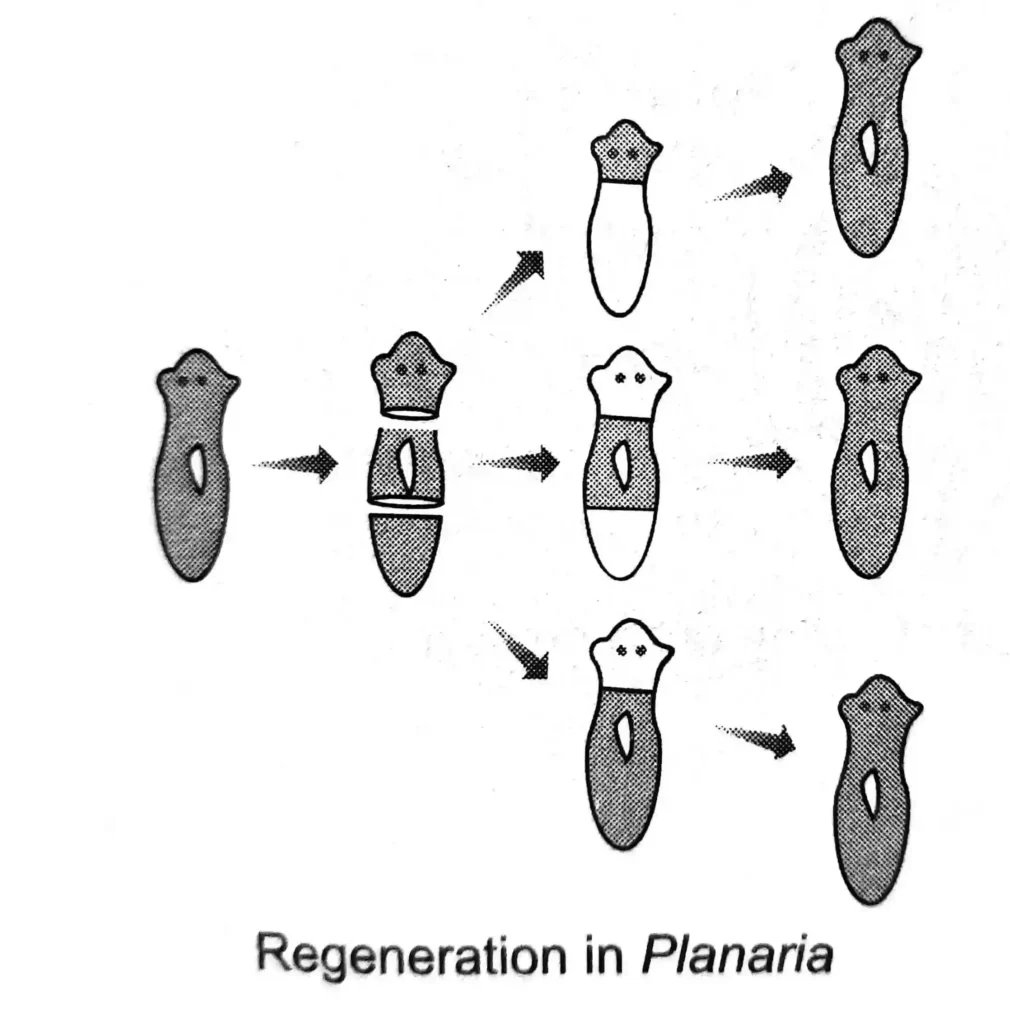
(iii) Regeneration. In this process, all fragments or parts that are separated from the body develop in new animals, e.g. sponge, Planaria, Hydra, etc.

(iv) Budding. A daughter organism is formed from a small projection known as bud. It develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell divisions of the parent body. When fully grown, it detaches to grow into a new independent individual, e.g. Hydra.


(v) Vegetative Propagation. The process of obtaining a complete plant from any vegetative part of a plant is called vegetative propagation. This is mainly of two types
(a) Natural Vegetative Propagation The vegetative propagation that occurs automatically in plants is called natural vegetative propagation. It can be achieved by root, stem, leaf, etc, e.g. Bryophyllum.


(b) Artificial Vegetative Propagation The artificially made vegetative propagules in plants by humans, is called artificial vegetative reproduction, e.g. cutting, layering, grafting, etc.
Grafting A small part of stem from one plant without roots (scion) is attached to the part with root (stock) of another plant.
Layering The development of roots on a stem, while the stem is still attached to the parent plant is called layering.
Tissue culture It is a technique used for growing new plants using living tissues (like flower buds, stems, growing tips? leaves, etc.) in vitro in an artificial culture medium.
Using this technique, a large number of plants can be developed from a single parent.
(vi) Spore Formation It is a type of asexual reproduction where blob-like structures called sporangia are involved. These cells or spores have the ability to germinate under favorable conditions forming new plants, e.g. Rhizopus.


ll. Modes of Sexual Reproduction
In this type of reproduction, both sexes, i.e. male and female are involved. Sex cell or gatnete of one parent (male) fuses with the sex cell or gatnete of another parent (fenmle). This results in production of a new cell called zygote.
Thus. the sexual nmode of reproduction involves two Imior processes
(i) Formation of gametes by meiosis
(ii) Fusion of gametes
1. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Angiosperms bear the reproductive parts within the flower and their seeds are enclosed in a fruit, Most plants have both male and female reproductive organs in the same flower and are known as bisexual flowers.
While others have either male or female reproductive parts in a flower known as unisexual flowers.
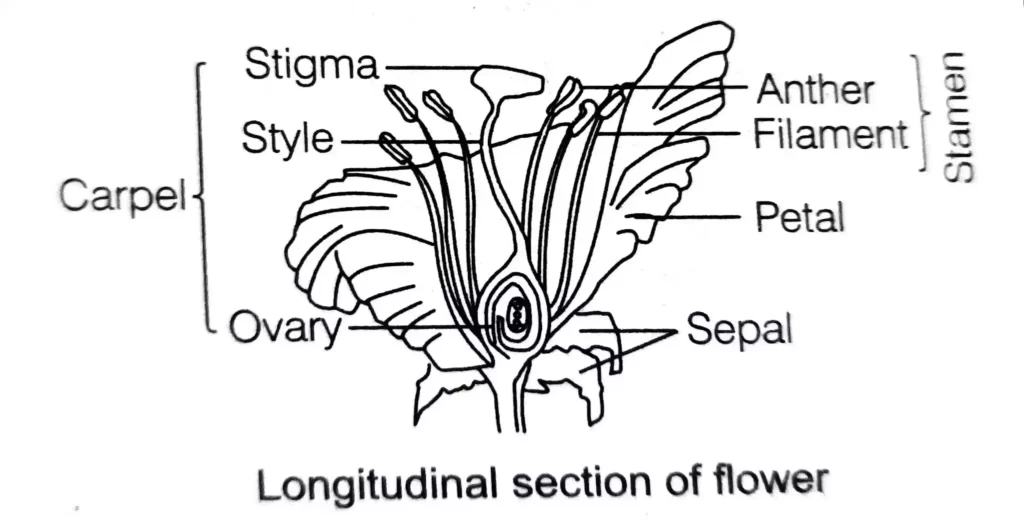
A flower comprises four main parts, i.e. sepals, petals, stamens and carpels. Stamens and carpels are the reproductive parts of a flower.
Stamen. It is the male reproductive part of the flower.
Anther It is a bilobed structure containing two pollen sacs present at the tip of stamen. These produce pollen grains that are yellowish in color
Carpel (Pistil) It is the female reproductive part, which is present in the center of the flower. It comprises of three parts
- Stigma It is the terminal part of the carpel which may be sticky. It helps in receiving the pollen grains during pollination.
- Style It is the middle elongated part of the carpel. It helps in the attachment of stigma to the ovary.
- Ovary. It is the swollen bottom part of carpel. It contains ovules having an egg cells (female gamete)

Pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of the stamen to the stigma of a flower is termed as pollination. The pollen grains can be transferred by various agents like wind, water, insects and animals.
Pollination usually occurs in two ways
- Self-pollination. The pollen from the stamen of a flower is transferred to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of same plant.
- Cross-pollination The pollen from the stamen of a flower is transferred to the stigma of another flower of different plant of the same species.
Fertilization
It is the process of fusion of male and female gametes. It gives rise to a zygote. As soon as the pollen lands on suitable stigma, it reaches the female germ cells in the ovary. This occurs via pollen tube.
The pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain, travels through the style and finally reaches the ovary.
After fertilization, the ovule develops a rough coat around itself and gets converted to seeds and the ovary ripens as fruit.
The seed contains a future embryo that grows under suitable conditions (germination). The fertilization in the flowering plant is shown in the given figure.


2. Sexual reproduction in human being
Human being can reproduce sexually after attaining puberty. It represents period of adolescence when reproductive organ start developing and sexual maturity is attained.
Some changes during puberty are common in males and females such as hair growth in armpit and genitals oily skin, acne etc.
Specific changes in boys include facial hair growth, hoarse voice, etc. In girls these changes are enlargement of breast size beginning of menstruation etc.
Click Below To Learn Term 2 Syllabus All Chapters
- Chapter 4: Carbon And Its Compounds Notes / Questions
- Chapter 5: Periodic Classification of Elements Notes / Questions
- Chapter 8: How Do Organism Reproduce Notes / Questions
- Chapter 9: Heredity And Evolution Notes / Questions
- Chapter 12: Electricity Notes / Questions
- Chapter13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Notes / Questions
- Chapter15: Our Environment Notes / Questions
Human Reproductive System
The system of organs required by males and females for the process of sexual reproduction is called reproductive system,
Male Reproductive System It includes parts which produce the germ cells and those, deliver these cells at the site of fertilisation.
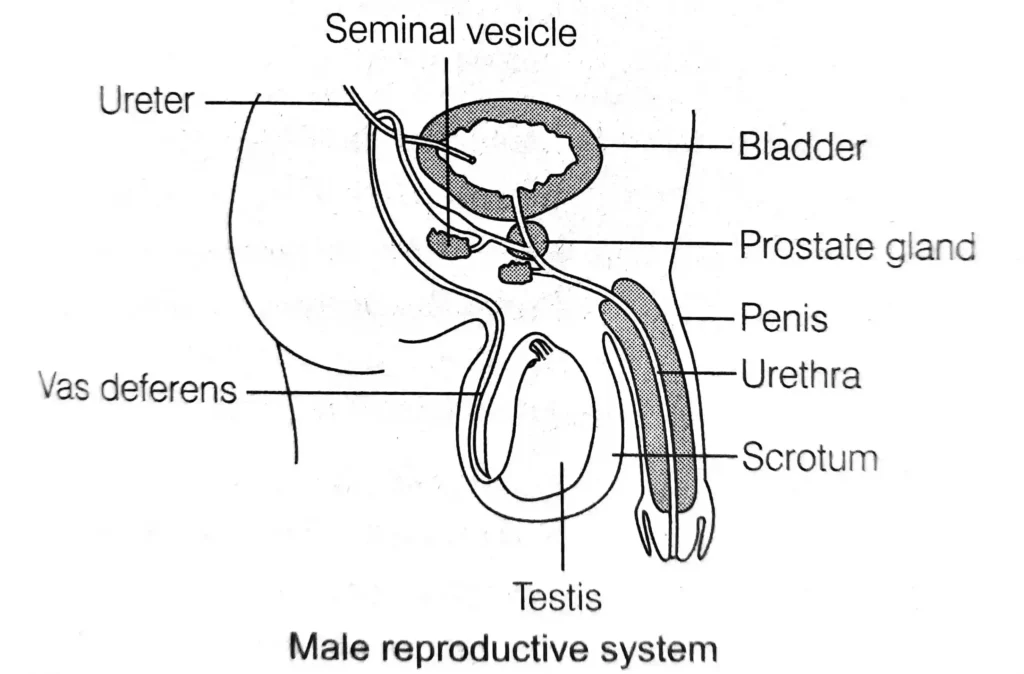

Parts and Details of the Male Reproductive System
Testes
- Paired, oval-shaped male sex organs.
- Consist of seminiferous tubules, where the sperms are produced.
- Produce a male sex hormone called testosterone, which brings about changes in appearance of boys at puberty
Scrotum
- Small pouch that contains testis.
- Present outside the abdominal cavity. As sperms are formed here, this requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature.
Vas deferens Tube-like structure which connects testis to the urethra deferens in order to allow the passage of semen.
Urethra Common passage for both the spertus and urine. It never carries both of them at the same time.
Prostate gland seminal and Seminal vesicles
- Secretes seminal fluid and nutrients.
- Fluid and nutrients combine with sperm to form semen. Milky vicious fluid contains Fructose, protein and other chemicals foundation and stimulating semen.
Penis
- External male genital organ.
- Transfers sperm into the vagina of the female during copulation.
Sperms
- Tiny and motile bodies that use their long tail to move through the female reproductive tract.
(ii) Female Reproductive System
It includes internal and external sex organs that function in reproduction of new offspring. In human, female reproductive system is immature at birth to maturity at puberty to be able to able to produce gametes, and carry a fetus.
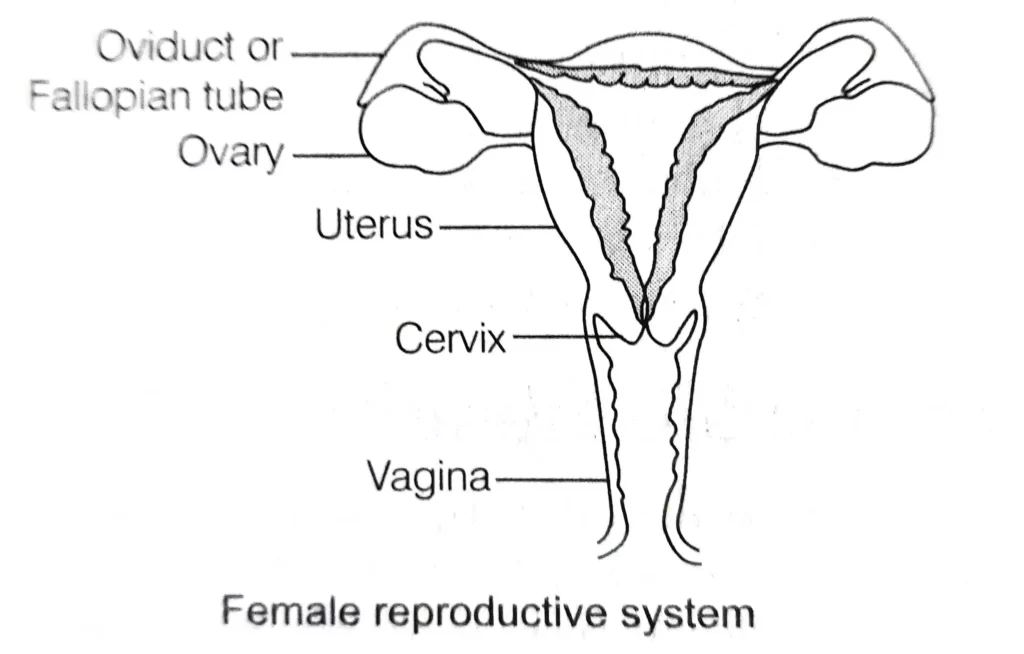

Parts and Details of the Female Reproductive System
Ovaries
- Paired, oval-shaped organs located in the abdominal cavity near the kidney.
- Produce thousands of ova or egg cells.
- Secrete female sex hormones like oestrogen and progesterone.
Oviduct (Fallopian tube)
- It has a funnel-shaped opening near the ovary.
- Carries ova or egg from ovary to the uterus.
- It is the site of fertilization.
- These open into the uterus from both the sides.
Uterus (womb)
- Hollow, pear-shaped, bag-like structure.
- The growth and development of the fetus takes place.
Cervix.
It is the lower and the narrower portion of the uterus which opens into the vagina.
Vagina. Receives the sperm from the male partner. Serves as a birth canal.
Fertilization and Post-Fertilisation
Changes
- Fusion of sperm with ovum is called fertilization. It results in the formation of diploid zygotes. This process takes place in the oviduct or Fallopian tube. The formation of embryos is the result of cleavage and growth in zygote.
- The embryo sinks downward, reaches into the soft uterine lining and gets embedded. This process is known as implantation.
- A disc-like structure called placenta grows between the uterine wall and embryo. It has finger-like projections called villi, which provide surface area for the exchange of nutrients, oxygen and waste products between the embryo and the mother.
Childbirth (after a gestation period of approximately 9 months) occurs by strong rhythmicI contractions of uterine muscles.
Menstruation
In the absence of fertilization, the uterine lining, which is thick and spongy to receive a fertilized egg, is no longer required. It sheds out blood and mucus which lasts for about 2-8 days acnl occurs every month. This phase is known as menstruation.
Reproductive Health
It can be defined as the state of physical, mental and social fitness to lead a healthy reproductive life. Good reproductive health provides both male and female with
- the fertility control methods.
- awareness about how to limit their family size.
- protection from infection and sexually transmitted diseases.
Sex Ratio
The ratio of the number of females to the number of males in a population is known as sex ratio. A balanced female-male sex ratio is necessary for a healthy society.
Population Size
The rates of birth and death in a given population determine its size. The population size increases if the birth rate is higher than the death rate and vice-versa.
Methods of Family Planning
The sexual act always carries the risk of potential pregnancy. In order to avoid unplanned pregnancies, many ways have been devised, which are called contraception or birth control methods.
Female Foeticide
The killing of an unborn girl child is called female foeticide. It is happening because of misuse of ultrasound technique by which
people get to know the sex of the child. If it is female, they get it removed by surgery.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) are caused by different pathogens transmitted by an intimate contact between healthy person and an infected person.
Also Read Chapter 5 How Do Organism Reproduce Notes Click Here
Frequently Asked Questions
Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction ? (NCERT)
Ans. The importance of DNA copying during reproduction are
(i) It is responsible for the transmission of parental characteristics to the offsprings.
(ii) During DNA copying in reproduction, the changes occur due to the inheritance of traits from both the parents. This leads to certain genetic variations, which are useful for the evolution of species over a period of time.
2. Why is variation beneficial to the species, but not necessary for the individual?
Ans. Variations allow organisms to exist in diverse habitats or niches. In its absence, a species may remain restricted to a particular area. If this area gets drastically altered due to various natural or man-made causes, the species may be wiped out.
However if some variations are present in few individuals it would help them to colonize other habitats and survive.
But if variations are present in a single organism, there would be a very little chance for it to survive and species are lost forever.
Hence, variations is beneficial to the species but not necessary for the individuals
3. What is a clone? Why do offspring formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity? (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. Clones are the offsprings produced by one parent through sexual reproduction. These are genetically identical to the parents; the clone pauses an exact copy of the DNA of their parent and hence shows remarkable similarity to the parent and to one another.
4, Colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water, but multiply in sugar solution. Give one reason for this. (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. When the colony of yeast is in water, it does not get any nutrition. Sugar solution on the contrary provides nutrition. As the yeast gets nutrition and thus energy, it grows and begins to produce buds. This is why colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water, but multiply in sugar solution.
5. Illustrate with example, the division and fragmentation method of reproduction in living organisms.
Ans. Multicellular organisms like filamentous algae (Spirogyra) and sea animal called sea anemone on maturation breakup into two or more small fragments or pieces. Each fragment subsequently grows to form a complete new organism. This type of asexual reproduction is known as fragmentation
6. List two advantages of vegetative propagation over other modes of reproduction.
Ans. Two advantages of vegetative propagation are as follows
(i) Vegetative reproduction is easier and faster methods of reproduction.
(ii) It is useful in those plants/animals, which cannot reproduce sexually.
7. Name a plant in which layering produces a new plant.
Ans. Layering is a type of vegetative propagation, e.g. lemon, rose, jasmine, strawberry, etc., can produce new plant by the process of layering.
8. Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of suvival, the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your answer. (CBSE 2018)
Ans. The main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction involves the production and union of gametes in the process of fertilisation in sexually reproducing organisms which do not occur in asexual mode of reproduction.
Sexual reproduction is considered to be superior over asexual reproduction as it leads to variations, while asexual reproduction does not induce variations among progeny individuals.
Advantages of variations in individuals are
(i) It brings adaptation in individuals.
(ii) It helps in the survival of species.
(iii) It is the basis of evolution.
Hence, the species that reproduce through sexual reproduction have better chances of survival,
9. In tobacco plants, the male gametes have twenty four chromosomes. What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete? What is the number of chromosomes in the zygote? (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. The number of chromosomes in the female gamete would be the same as that in the male gamete, i.e. it will have 24 chromosomes. The number of chromosomes in the zygote would be double the number present in the gainete and hence, it would be 48.
10. Differentiate between self-pollination and cross pollination.
Ans. Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a flower. It is of two types
(i) Self-pollination. Transfer of pollen from the stamens Of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or on the stigma of other flower of the same plant.
(ii) Cross-pollination. Transfer of pollen from the stamens of a flower to the stigma of different flowers of different plailt of same species.
11. In a bisexual flower inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation. (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. A bisexual flower has the the male as well as female reproductive organs. If the young stamen (male unit) is removed artificially the flower still has its pistil (female unit) intact therefore cross pollination can occur.
When the pollen grains from the anther of another flower are transferred to the stigma of this flower with the help of pollination agent such as insects these winds and water it causes cross pollination after the pollen grains fall on stigma the next step is fertilization followed by formation of fruits and seeds.
12. Differentiate between unisexual and bisexual flowers and give one example of each.
Ans. Stamens and carpels (pistils) are the reproductive organ of a flower organs by which sexual reproduction in flowering plants takes place. Most plants have both male and female reproductive organs in the same flower and are known as bisexual flowers e.g. Lily, roses etc. while others have either male or female reproductive parts in a flower known as unisexual flower e.g. papaya watermelon etc.
13. (i) List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny fonned by sexual reproduction. (CBSE 2016)
(a) Name the part marked as A in the diagram.
(b) How does A reach part B?
(c) State the importance of the part C.
(d) What happens to the part marked as D after fertilization is over?
Ans. . (i) Variations appear among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction due to the following reasons
(a) Sexual reproduction results in new combinations of genes that are brought together during the formation of gametes by meiotic divisions (I and Il).
(b) The combination of two sets of chromosomes, one between the homologous chromosome arms set from each parent during zygote formation, leads to variation within a species.
(ii) (a) A—Pollen grain
(b) Pollen grain reaches part B, i.e. stigma by pollinating agents such as insects, wind, water, etc. This process is known as pollination.
(c) Part C is the pollen tube. It allows the passage for the male gametes to reach the ovary having female gametes for fertilization.
(d) Part D, i.e. female gamete or egg cell that forms zygote after fertilization.
14. (i) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma of a flower and mark on it the following organs/parts (CBSE 2020)
(a) Pollen grain
(b) Pollen tube
(c) Stigma
(d) Female germ cell
(ii) State the significance of pollen tube.
(iii) Name the parts of flower that develop after fertilization into
(a) Seed (b) Fruit
Ans. 14. (i)


(ii) The pollen tube takes its origin from the intestines of pollen grains. It grows through the style and reaches the micropyle of the ovule. It carries male nuclei to the ovule for fertilization.
(iii) (a) Ovule develops into seed.
(b) Mature ovaries develop into fruit.
15, Why cannot fertilization take place in flowers if pollination does not occur? (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. In a flower, fertilization requires both male and female gametes. So, it is necessary that the male gamete reaches the female gamete. This can happen when the pollen grains are transferred to the stigma through any means of pollination.
Hence, fertilisation cannot take place in flowers if pollination does not occur due to absence of pollen lube (i.e. the male gamete).
16. How are general and sexmal maturation different from each other?
(NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. General growth refers to different types of developmental process in the like increase in height, weight gain, changes in shape and size of the body. During this phase, the reproductive organs develops at a slower rate,
During sexual maturation, the changes that occur prepare the body for sexual reproduction. These are specific changes reflected at puberty like cracking of voice new hair patterns development of breast in female etc.
17. Draw the human female reproductive system and label the following parts
(i) Which organ produces ovum?
(ii) Where does fertilization take place?
(iii) Where does implantation of embryos take place? (2013, 2019)
Ans.


(i) Ovum is produced by ovaries which are paired, oval-shaped organs.
(ii) Oviduct or Fallopian tubes are the site of fertilization. They have a funnel-shaped opening near the ovary and carry ova or egg from ovary to uterus.
(iii) Implantation refers to the embedding of the embryo in the thick lining of the uterus.
18. List two functions of ovary of female reproductive system. (CBSE 2016)
Ans. Ovary in females is responsible for the production of female gametes (ova) and also produces female sex hormones, i.e. oestrogen and progesterone.
19. A newly married couple wants to conceive as quickly as possible.
What is the first sign of pregnancy shown by the woman ?
Ans. The absence of a menstrual cycle may be the first indication of pregnancy in a woman.
20. What changes are observed in the uterus if fertilization does not occur? (Exemplar)
Ans. If the egg is not fertilized, it lives for about one day. Since, the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilized egg. Its lining becomes thick and spongy, which is required for nourishing the embryo.
If fertilization, however, does not take place this lining is not needed in the absence of fertilization and it slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus. This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as the menstruation cycle and usually lasts for about 2-8 days.
21. How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body? (NCERT, CBSE 2015)
Ans. The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. This is a disc-like tissue which develops between the uterine wall and embryo.
As mother eats, the food passes through the digestive system where it breaks down into small particles. These nutrients travel through the mother’s bloodstream and get exchanged with the bloodstream of the fetus through the placenta.
22. What is the function of the umbilical cord ?
Ans. The umbilical cord contains blood vessels which supply blood between the fetus and the placenta.
23. Why are testes located outside the abdominal cavity?
Ans. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature.
24. Trace the path of sperm during ejaculation and mention the glands associated with the male reproductive system and their functions. (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. Path of sperm during ejaculation Formation of sperms takes place in testis. Sperms come out from testis into the vas deferens, It then unites with another tube called urethra coming from the urinary bladder. Along the path of vas deferens. glands like the prostate and the seminal vesicle add their secretion, so that sperms are in fluid medium to make their transport easier. This fluids also provides nutrition. Glands associated with Male reproductive system are:
Testes it secrets the male sex hormone testosterone
Prostate gland it makes the semen medium alkaline
Cowper’s Gland. Its secretion of this gland lubricates the urethra before ejaculation Seminal vesicle It adds fluid content to semen
25. What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote? How is the sperm genetically different from the egg?
Ans. The ratio of chromosome number between egg and its zygote is 1 : 2. An egg is a female gamete and it has haploid nurnber of chromosomes. During fertilization, it fuses with male gametes (also having haploid number of chromosomes) to form a zygote which now has diploid number of chromosomes.
Sperms and eggs are genetically different in terrns of nature of sex chromosome. The sperm contains either X or Y-chromosome, whereas an egg will always have an X-chromosome.
26. State any two methods of contracting an STD other than the se-wal contact.
Ans. Two methods of contracting an STD other than the sexual contact are as follows
(i) Sharing needles with an infected person.
(ii) Transfusion of STD unscreened blood.
27. How can people praetiee safe sex to avoid contracting an STD ?
Ans.
27. People can practice safe sex by using condoms as it acts as barrier method of contraception and does not allow entry of semen into vagina. Therefore, prevent STDs and avoid chances of pregnancy.
28. If a woman is using a copper-T, will it help in protecting her from sexmally transmitted disease. (NCERT)
Ans.
28. No, copper-T does not prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases. Copper-T only prevents implantation. The only safe method that can be used to prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases is condoms.
29. Write a short note on family planning,
Ans. Family planning refers to the regulation of conception by the use of contraceptive methods or devices to limit the number of offspring.
The methods used to prevent the occurrence of pregnancy are called contraceptive methods. These can be barrier, hormonal, chemical and surgical methods.
30. (i) ‘Use of a condom is beneficial for both the sexes involved in a sexual act’. Justify this statement. Give two reasons.
(ii) How do oral contraceptives help in avoiding pregnancies?
(iii) What is sex selective abortion? How does it affect a healthy society? State any one consequence) (CBSE 2020)
Ans. (i) Use of a condom is beneficial for both the sexes involved in a sexual act. It is because of the following facts
(a) It prevents pregnancy which is not desired by a couple.
(b) It saves both the partners froun sexually trausnlitted diseases like AIDS, etc.
(ii) Oral contraceptives are the hormonal pills which at? taken by the females after their menstruation encls up. It is taken for 21 days daily. It changes the cyclic events of ovulation etc. So mature ovum is not available for fertilization
(iii) Sex selective abortion means the foetus is female, it is killed and extracted. This creates an imbalanced in the society by disturbing the sex ratio.
31. What are the various ways to avoid pregnancy?
Elaborate any one method (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. Ways to avoid pregnancy are called contraceptives methods.
It includes a number of ways such as
(i) Mechanical barrier; e.g. condom
(ii) Drugs(oral pills for female).
(iii) IUCD, e.g. copper-T.
(iv) Surgical method for permanent contraception,
Mechanical Barrier There are a number of methods that create barrier between sperm and egg some of them are as Follows
Condom It is a fine rubber balloon-like structure worn over the penis during sexual intercourse. Semen is collected in it and not discharged into the vagina. This method also prevents the spread of STDs like AIDS, syphilis, etc.
Diaphragms or Caps It can be fitted in the cervix of a woman to prevent semen from reaching the Fallopian tube.
Long Answer Type Questions
32. Reproduction is essentially a phenomenon that is not for the survival of man but for ‘the stability of a species. Justify (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. All the living organisms need energy for their survival and growth. This energy is obtained from various life processes such as nutrition, excretion and respiration.
Thus, these phenomena are essential for the survival of an individual. Compared to these life processes, reproduction is not essential for survival of an individual.
It is basically important for continuity of the generation of an organism or species as DNA copying during reproduction helps to produce similar individuals as their parents to maintain stability of a species.
33. ‘Reproduction helps in providing stability to the population of a species’. Justify this statement.
Ans. A species occupies a well-defined niche in an ecosystem, using its ability to reproduce. During reproduction, copies of DNA pass from one generation to the next. This copying of DNA takes place with consistency in reproducing organisms and this is important for the maintenance of body design features (physiological as well as structural) which allows the organism to use that particular niche. Reproduction is therefore linked to the stability of the population of a species.
34. (i) Name the mode of reproduction of the following organisms and state the important feature of each mode
(a) Planaria (b) Hydra (c) Rhizopus
(ii) We can develop new plants from the leaves of Bryophyllum. Comment.
Ans. (i) (a) Planarian—Regeneration
(b) Hydra—Budding
(c) Rhizopus—Sporulation
(ii) The leaves of Bryophyllum bear vegetative adventitious buds which on separation can give rise to new plants.
35. Explain the fertilization process in plants with the help of a labeled diagram of a longitudinal section of a flower.
Ans. Stamens and carpels are the reproductive parts of a flower.
Stamen is the male reproductive part of the flower.
Anther is a bilobed structure containing two pollen sacs present at tip of stamen. These produce pollen grains that are yellowish in color.
Carpel (Pistil) is the female reproductive part, which is present in the center of the flower. It comprises of three parts:
(i) Stigma It is the terminal part of carpel which may be sticky. It helps in receiving the pollen grains during pollination.
(ii) Style It is the middle elongated part of the carpel. It helps in the attachment of stigma to the ovary.
(iii) Ovary It is the swollen bottom part of the carpel. It contains ovules having an egg cell (female gamete).


Fertilization is the process of fusion of male germ cells with the female gamete. It gives rise to a zygote. As soon as the pollen lands on suitable stigma, it reaches the female germ cells in the ovary. This occurs via a pollen tube. The pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain, travels through the style and finally reaches the ovary,
36. Define pollination. Explain the difference of pollination. List two agents of pollination. How does suitable pollination lead to fertilization? (CBSE 2019)
Ans. The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of the stamen to the stigma of a flower is termed as pollination. There are two types of pollination
(i) Self-pollination The pollen from the stamen of a flower is transferred to the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant.
(ii) Cross-pollination The pollen from the stamen of a flower is transferred to the stigma of another flower of different individuals of the same species.
The pollen grains can be transferred by various agents like water, insects and animals. As soon as the pollen lands on suitable stigma, it reaches the female germ cells in the ovary. This occurs via a pollen tube.
The pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain, travels through the style and finally reaches the ovary where it fuses with female gamete (ovule) to give rise to zygote.
Hence, pollination is followed by fertilization in plants.
37. Distinguish between pollination and fertilization. Mention the site and product, or in a flower. Draw a neat, labeled diagram of a pistil pollen tube and its entry into the ovule. (NCERT Exemplar)
Ans. Distinguishes between pollination and fertilization are as follows:
| Pollination | Fertilization |
| It is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma. | It is the fusion of male and female gametes. |
| It is a physical process. | It is a biological process. |
The site of fertilization is ovule in the ovary.
The product of fertilization is a zygote.
38. Trace the change that takes place in a flower from gamete formation to fruit formation. (CBSE 2020)
Ans. Stamen is the male reproductive part and it produces pollen grains. The ovary contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell.
The pollen grain is transferred from the stamen to stigma. It is transferred if pollen occurs in the same flower, it is referred to as self-pollination.
On the other hand, if the pollen is transferred from one flower to another, it is known as cross pollination. After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, it has to reach the female germ cells which are present in the ovary.
For thus, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary.


Germination of pollen on stigma
The male germ cell produced by pollen grain fuses with the female gamete precut in the ovule. This fusion of germ cells is called fertilization and gives rise to the zygote.
After the fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a hard coat and is gradually converted into a seed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form fruit. Meanwhile the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off.
39. Based on the given diagram, answer the questions given below.


(i) Label the parts A, B, C and D.
(ii) Name the hormone secreted by testis and mention its role.
(iii) State the functions of B and C in the process of reproduction. (CBSE 2020)
Ans.
(i) A—Ureter B—Seminal vesicle
C—Urethra D—Vas deferens
(ii) Testosterone hormone is secreted by testis. It controls spermatogenesis (formation of sperm) and secondary sexual characters in male adolescents.
(iii) Seminal vesicle B temporarily stores sperm.
Urethra (C) It transports and releases urine and sperms outside the body.
40. (i) Identify the given diagram. Name the parts labeled as A to E. (CBSE 2019)


(ii) What is contraception? List three advantages of adopting contraceptive measures.
Ans. (i) The given figure represents the female reproductive system. The parts labeled as A-E are
A. Oviduct or Fallopian tube
B. Ovary C Uterus
D. Cervix E. Vagina
(ii) The prevention of pregnancies by using artificial methods is called contraception.
Advantages of using contraceptive measures are
(a) To control family size, population rise or birth rate. This is done by creating awareness about small families using contraceptive measures.
(b) To prevent chances of meeting female, egg and male sperm, thus preventing future unwanted pregnancies.
(c) Use of barrier methods of contraception protects both the partners from contracting sexually transmitted diseases like AIDS.
41. (i) Write the function of the following parts in the human female reproductive system.
(a) Ovary (b) Oviduct (c) Uterus
(ii) Describe in brief the structure and function of placenta. (CBSE 2018)
Ans. (i)


(ii) Structure of Placenta It is a disc between uterine wall and embryo which is embedded in the uterine wall. It
contains Villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side, blood spaces are present, which surround the villi.
Functions of Placenta It provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. It also removes the waste generated by the embryo, transferring it to the mother’s blood.
42. Trace out the movement and fate of eggs in the female body.
Ans. Movement and fate of egg in female body


43. Give reasons,
(i) Placenta is essential for fetal development
(ii) Blocking of vas deferens prevents pregnancy.
(iii) Wind acts a pollinating agent
(iv) Use of condoms prevents pregnancy.
(v) Blocking of Fallopian tubes prevents pregnancy.
Ans. (i) Placenta is extremely essential for fetal development because it helps in nutrition, respiration, excretion, etc., of the fetus through the maternal supply.
(ii) Blocking of vas deferens prevents passage of sperms, hence, there is no fertilization so it prevents pregnancy.
(iii) Wind acts as a pollinating agent because it helps in transfer of light weighted pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower.
(iv) Condoms prevent the entry of sperms into vagina, hence preventing pregnancy.
(v) If Fallopian tube is blocked, sperm and egg do not meet or fuse and fertilization does not take place.
44. List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country.
Ans. Reproductive health is a state of physical, emotional, inental and social well-being in relation to sexuality.
Significance of reproductive health in a society
(i) It prevents the spread of various Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD).
(ii) Proper medication and checkups will help in the production of healthy
(iii) Better sex education and awareness help in tnailltaining the population and prevent the population explosion.
(iv) Unwanted pregnancies are avoided.
The reproductive health in India has improved tremendously over the past 50 years, The areas in which reproductive health has improved includes
(i) Prevention of unwanted pregnancies by using contraceptives have shown the development of health in women.
(ii) Awareness of advantages of small families by using contraceptives has led to growth of the family,
Case Based Questions
45. Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to (v) given below
Salman soaked a few seeds of Bengal gram (chana) and kept them overnight. Next morning, he drained the excess water and covered the seeds with a wet cloth. He then left the seeds for a day.
After one day, he opened the seeds into two parts and carefully observed the different parts.


(i) Which part of the flower develops into seed?
(ii) Where does the energy required for germination of seeds come from?
(iii) Which part of the seed emerges first?
(iv) Define germination.
(v) What are the necessary conditions for seed germination ?
Ans. (i) The ovules present in ovary ol’ a (lower develops into seeds
(ii) Cotyledons of seed store food which fulfill the energy requirement for seed germination (iii) Radicle or future root of the plant amounts out the first from the germinating seed
(iv) The process of developing seed into a seedling under appropriate conditions is known as germination
(v) All seeds need water oxygen and proper temperature in order to germinate
46. Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to (v) given below
As soon as boys and girls reach adolescent age, certain changes start happening in their bodies under the influence of sex hormones produced in their bodies. These changes are mostly related to height, size, voice pitch, physical attributes, etc. The table below shows the average height of boys and girls upto the age of 18 years.


(i) State the changes happening in adolescent boys and girls.
(ii) When does the most rapid growth take place?
(iii) The increase in height in girls almost ceases at what age?
(iv) Significant spurt in increase of height of boys occurs at what age?
(v) What are the changes that are common in both boys and girls at the age of adolescence?
Ans. (i) The changes happening in adolescent boys and girls are: The mustache starts appearing in boys and their voice becomes hoarse. There is onset of menstrual cycle in girls and their mammary glands start developing.
(ii) Most rapid growth takes place within one year after the birth of a baby.
(iii) The increase in height of girls increases at the age of 15 years.
(iv) In boys, significant spurt in height occurs at the age of 11-12 yrs.
(v) Both boys and girls grow body hair in their pubic area, as well as under the arms and on the legs at the age of adolescence.
47. Read the and answer the questions from (i) to (v) given below.
The male has reproductive organs or genitals that are both inside and outside the pehis. The male genitals include the testicles, the duct system, accessory glands and the penis.
In male who has reached sexual maturitv, the two oval-shaped testicles make and store millions of tiny sperm cells.
Testicles are also part of the endocrine system.
#####
(i) Name the organ that acts as both endocrine and exocrine gland?
(ii) How is the sperm genetically different from the egg?
(iii) What is semen?
(iv) A man wants a surgical operation for family planning. Which part of his reproductive system needs to be operated on?
(v) What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote?
Ans. (i) The two main functions of the testes (F) are to produce sperm and to produce the male sex hormones (testosterone). This makes the testis both an endocrine and exocrine gland.
(ii) The sperm and eggs are genetically different terms of nature of sex chromosome. The sperm contains either X or Y-chromosome whereas an egg will always have an X-chromosome.
(iii) Semen is a fluid which contains sperm cells and secretion of accessory glands. It is a milky, viscous fluid containing fructose, proteins and other chemicals for nourishing sperms.
(iv) Vasectomy is a form of male birth control that cuts the supply of sperm to semen. It is done by cutting and sealing the tubes that carry sperm, i.e. vas deferens (H).
(v) Fusion of a sperm and an egg leads to the formation of a zygote. Therefore, a zygote is diploid in nature,
i.e. 2n, whereas a sperm and an egg are haploid in nature, i.e. n. Hence, the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote is 1 : 2.
48. Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to (v) given below
The term Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) refers to a condition passed from one person to another through sexual contact. However, it is not the only way STDs can be transmitted.
An STD develops without any symptoms early on, or if any symptoms appear they are often dismissed as regular infections.
At present, there are several types of STDs known which are caused by different types of pathogens.
Some of these STDs are curable, while other are not. The only full proof way of avoiding an STD is to practice safe sex.
(i) Give two examples of STDs.
(ii) Do you think like viruses, bacteria can also cause an STD? Give an example.
(iii) Name a of contraception wllieli protects us from acquiring sexually transmitted diseases?
(iv) What is IUCD? Give one example.
(v) Emergency contraceptives may prevent pregnancy if used within 72 hrs of ——-
Ans. 48, (i) (a) AlDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) (b) Genital warts
(ii) Yes, bacteria are also known to cause STDs. For example, Syphilis is an STD caused by bacteria, Treponema, pallidum.
(iii) Condoms protect us from acquiring STDs. It also helps in avoiding pregnancy.
(iv) IUCD stands for Intra-Uterine Contraceptive Device. It is used to prevent pregnancy, e.g. Copper-T
(v) Emergency contraceptives may prevent pregnancy if used within 72 hrs of coitus/intercourse.
Click Below To Learn Term 2 Syllabus All Chapters
- Chapter 4: Carbon And Its Compounds Notes / Questions
- Chapter 5: Periodic Classification of Elements Notes / Questions
- Chapter 8: How Do Organism Reproduce Notes / Questions
- Chapter 9: Heredity And Evolution Notes / Questions
- Chapter 12: Electricity Notes / Questions
- Chapter13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Notes / Questions
- Chapter15: Our Environment Notes / Questions
Final Words
From the above article, you have practiced Class 10 chapter 8 How do organism reproduce notes and questions. We hope that the above-mentioned notes and Q & A for term 2 will surely help you in your exam.
If you have any doubts or queries regarding Class 10 chapter 8 How do organism reproduce notes and questions with Answers, feel free to reach us and we will get back to you as early as possible.
Click Below To Learn Science
Term-1 Syllabus Chapter wise MCQs