Last updated on July 14th, 2024 at 05:42 pm
Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ
Alcohol is a class of organic compound that has a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom in a hydrocarbon chain
Phenol is another class of organic compound in which the hydroxyl group is attached to the carbon in an aromatic ring.
Ether is a class of organic compound in which an oxygen atom is bonded to two allyl or alkyl groups.
Below are some of the very important NCERT Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 with Answers. These Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs have been prepared by expert teachers and subject experts based on the latest syllabus and pattern of CBSE Term 1 examination.
We have given these Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Chemistry MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept.
MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry are very important for the latest CBSE Term 1 and Term 2 pattern. These MCQs are very important for students who want to score high in CBSE Board, NEET and JEE exam.
We have put together these NCERT MCQ Questions of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 with Answers for the practice on a regular basis to score high in exams. Refer to these MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Note : – Answers after every 10 questions


Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ (1-10)
- Phenol, when it first reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid and then with concentrated nitric acid, gives
- 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzene
- o-Nitrophenol
- p-Nitrophenol
- Nitrobenzene
- The number of stereoisomers possible for a compound of the molecular formula


1 . 3 2. 2 3. 4 4. 6
- The compound which reacts the fastest with Lucas reagent at room temperature is
- Butan-1-ol
- 2-methyl-propan-2-ol
- 2-methyl-1-propan-1-ol
- Butan-2-ol
- Which of the isomers of nitrophenol is steam volatile?
- Ortho
- Para
- Meta
- None of these
- A compound develops red colour with a solution of ceric ammonium nitrate. The compound may be
- An alkene
- An alcohol
- A ketone
- An aldehyde
- Glycerol reacts with phosphorus triiodide to form
- Allyl alcohol
- Allyl iodide
- Acrolein
- 1,2,3-triiodopopane
- Choose the reagent to carry out the following reaction


1 . Bromine water 2. Bromine in CCl4
3. Either 1 or 2 4. Reaction is not possible
- Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form
- Azobenzene
- Benzene
- Benzyl alcohol
- Phenol
- Which of the following will not be soluble in sodium bicarbonate?
- 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol
- Benzoic acid
- o-Nitrophenol
- Benzenesulphonic acid
- Which of the following gives alkene with ethylene glycol?
- PCl3
- PI3
- PBr3
- None of these
Answers (1-10)
1 . (2)


-OH group is the ortho and para directing group, but -SO3H group being bigger preferably occupies the para position. As the temperature is not mentioned, ortho nitrobenzene will be more stable.
2. (3)
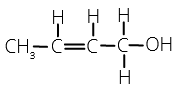

One chiral carbon means two enantiomers and two geometrical isomers (cis and trans) are also possible. So, a total of four isomers are possible.
3. (2)
Lucas test is used to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol. As tertiary alcohol is the most stable, it reacts the fastest with the Lucas reagent and causes turbidity. Then comes the secondary alcohol and at last, the primary alcohol. As 2-methyl-propan-2-ol is a tertiary alcohol, it will react the fastest with the Lucas reagent.


4. (1)
Ortho nitrophenol will be more volatile due to the presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding. Para nitrophenol has intermolecular hydrogen bonding which is comparatively forms much stronger bonds, due to which the boiling point will also increase.


5. (2)
An alcoholic group gives red colour with ceric ammonium nitrate.
6. (2)
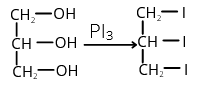

7. (2)
Bromine water
8. (4)
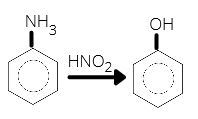

9. (3)
The reaction moves in forward direction if the reactants are more acidic than NaHCO3. As o-nitrophenol is less acidic than NaHCO3, it wont react.
10. (2)
Ethylene glycol + PI3 → Ethylene
Click Below To Learn Physics Term 1 Syllabus Chapter-Wise MCQs
Click Below To Learn Chemistry Term-1 Syllabus Chapters MCQs
- Chapter-1: Solid State MCQ
- Chapter-2: Solution MCQ
- Chapter-7: P-Block Element MCQ
- Chapter 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQ
- Chapter 11: Alcohols Phenols and Ether MCQ
- Chapter-14: Biomolecules MCQ
Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ (11-20)
- Which of the following is not true in the case of reaction with heated copper at 300℃?
- Phenol → Benzyl alcohol
- Primary alcohol → Aldehyde
- Secondary alcohol → Ketone
- Tertiary alcohol → Olefin
- 1-phenylethanol can be prepared by the reaction of benzaldehyde with
- Methyl bromide
- Ethyl iodide and magnesium
- Methyl iodide and magnesium
- Methyl bromide and aluminium bromide
- What is the reagent required in the following reaction


1 . Hydrogen peroxide 2. CrO3
3. Chromyl chloride 4. All of these
- In the following reaction, P is


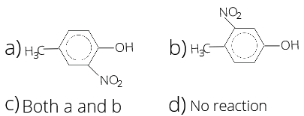

1 . (a) 2. (b) 3. (c) 4. (d)
- Dichloroacetic acid on hydrolysis gives
- Ethane-1,2-dione
- Formylmethanoic acid
- 2-Hydroxyethanoic acid
- Ethane-1,2-diol
- Identify X in the following reaction


1 . C2H5OC2H5 2. C6H5OC6H5
3. C6H5I 4. C6H5OC2H5
- Which of the following reagent convert the propene to 1-propanol?
- H2O, H2SO4
- Aqueous KOH
- MhSO4, NaBH4/H2O
- B2H6, H2O2, OH–
- Which of the following can not be formed by hydrolysis of alkenes?
- Ethanol
- Propanol
- Methanol
- None of these
- Decolourisation of KMnO4 solution takes place when it reacts with ethene. The final product of this reaction which is used as antifreeze is
- Propylene glycol
- Ethanol
- Propanol
- Ethylene glycol
- 1-Bromopentane on boiling with alcoholic potassium hydroxide gives
- Pentan-1-ol
- Pent-1-ene
- Pentan-2-ol
- Pent-2-ene
Answers (11-20)
11. (1)
Phenol can not be converted to benzyl alcohol because the oxidation of phenol can’t give benzyl alcohol.
12. (3)
When benzaldehyde reacts with methyl iodide and magnesium followed by hydrolysis, the formation of 1-phenylethanol takes place.


13. (1)


14. (1)


15. (2)
Formylmethanoic acid
16. (4)


17. (2)
Aqueous KOH
18. (3)
Hydrolysis of alkene mainly gives alcohol simplest alkene that is ethane on hydrolysis gives ethanol. So methanol can not be formed by hydrolysis of alkene.
19. (4)
Hydrolysis of ethene takes place in the presence of cold KMnO4 to form ethylene glycol (HOCH2-CH2OH).
20. (2)
When haloalkane is treated with conc. alcoholic solution of KOH, a molecule of hydrogen halide is eliminated to form alkene. The eliminated hydrogen atom comes from the B-carbon atom, so it is called B-elimination. Most highly substituted alkene is a major product.


Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ (21-30)
- Among ethanol, dimethyl ether, methanol and propanol, the isomers are
- Ethanol, dimethyl ether, methanol and propanol
- Ethanol and methanol
- Ethanol, dimethyl ether and methanol
- Ethanol and dimethyl ether
- Ether is obtained from ethyl alcohol in presence of H2SO4 at?
- 113 K
- 443 K
- 413 K
- 213 K
- Alkyl halides are converted into ether through
- Frankland reaction
- Williamson synthesis
- Fittig reaction
- Grignard reaction
- The compound having the lowest boiling point is
- H2O
- C2H5OH
- CH3OH
- CH3OCH3
- Which if the following pairs show ideal behavior?
- C6H5CH3 + C6H6
- CH3OH + H2O
- CH3COCH3 + CHCl3
- H2O + HCl
- One of the following which can not undergo dehydro-halogenation is
- Iso-propyl bromide
- Ethanol
- Ethyl bromide
- None of these
- Dehydration of alcohol is an example of
- Substitution reaction
- Elimination reaction
- Rearrangement reaction
- Addition reaction
- Which of the following is the most soluble in water?
- n-Butyl alcohol
- Isobutyl alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Secondary butyl alcohol
- Which of the following is not a character of alcohol?
- They are lighter than water
- Their boiling points rise fairly uniformly with increasing molecular weight
- Lower members are insoluble in water and organic solvents but solubility regularly increases with molecular weight
- Lower members have pleasant smell and burning taste, while higher members are odourless and tasteless
- Enzymes used in the fermentation of cane sugar to alcohol are
- Diastase, invertase
- Invertase, zymase
- Diastase, zymase
- Maltase, zymase
Answers (21-30)
21. (4)
Ethanol (C2H5OH) and dimethyl ether (CH3-O-CH3) have the same molecular formula but different functional groups, so they are isomers.
22. (3)
Ether is obtained from ethyl alcohol at 413 K.
23. (2)
Alkyl halides are converted into ether through Williamson synthesis.
24. (4)
Due to less amount of hydrogen bonding in ether, boiling point will be the less.
25. (1)
C6H5CH3 (Toluene) + C6H6 (Benzene)
26. (2)
Ethanol doesn’t have a halogen group attached. Hence, it can’t undergo dehydrohalogenation.
27. (2)
Dehydration of alcohol is an example of ꞵ-elimination.


28. (3)
Solubility decreases with an increase in size of the alkyl group which is a hydrophobic group, which makes the alcohol less hydrophilic.
In the case of isomers, the order of solubility is 3°>2°>1° due to increase in polar character.
29. (1)
Lower members are soluble in water and solubility decreases with increasing molecular mass because the length of hydrocarbon chain increases.
30. (2)
Invertase and zymase are used in the fermentation of cane sugar to alcohol.
Click Below To Learn Chemistry Term-1 Syllabus Chapters MCQs
- Chapter-1: Solid State MCQ
- Chapter-2: Solution MCQ
- Chapter-7: P-Block Element MCQ
- Chapter 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQ
- Chapter 11: Alcohols Phenols and Ether MCQ
- Chapter-14: Biomolecules MCQ
Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ (31-40)
- Cyclohexanol is a
- Primary alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Phenol
- Which of the following substances can not be used for the replacement of -OH group in organic compounds by Cl?
- S2Cl2
- SOCl2
- PCl3
- PCl5
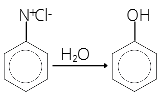
- The formation of phenol from benzene diazonium chloride is a
- Pyrolysis reaction
- Photosynthesis reaction
- Hydrolysis reaction
- Combustion reaction
- Sodium benzene sulphonate reacts with NaOH and then on acidic hydrolysis, it gives
- Benzoic acid
- Benzene
- Disodium benzaldehyde
- Phenol
- Wood spirit is known as
- Methanol
- Ethanol
- Acetone
- Benzene
- Carbinol is a trivial name of
- C2H5OH
- CH3OH
- HCOOH
- CH3COOH
- Which among the following reactions does not give methyl alcohol?
- The reaction of water gas with hydrogen at high temperature
- Alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide
- The reaction of ethylene with H2SO4 at 80℃
- Both 1 and 2
- The other name of syngas is
- Fuel gas
- Tear gas
- Producer gas
- Water gas
- 4-chloro-3,5-dimethyl phenol is called
- Chloramphenicol
- Paracetamol
- Barbital
- Dettol
- IUPAC name of m-cresol is
- 3-methylphenol
- 3-chlorophenol
- 3-methoxyphenol
- Benzene-1,3-diol
Answers (31-40)
31. (2)
In cyclohexanol, -OH is attached to a secondary carbon in the ring.
32. (1)
S2Cl2 can’t be used.
33. (3)

34. (4)
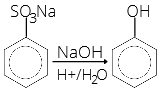
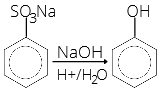
35. (1)
Methanol is known as wood spirit.
36. (2)
Carbinol is a trivial name of methanol (CH3OH).
37. (3)
The reaction of ethylene with H2SO4 at 80℃ gives
CH2CH2 + H2SO4 → CH3CH2OSO2OH
Water gas at high temperature gives
CO + 2H2 → CH3OH
Alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide gives methanol
CH3Br + H2O → CH3OH + HBr
38. (4)
The other name of syngas is water gas.
39. (4)
Dettol
40. (1)
3-methylphenol (CH3)C6H5OH
Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ (41-50)
- IUPAC name of picric acid
- M-nitrobenzoic acid
- 2,4,6–trinitrophenol
- Trinitrotoluene
- Trinitroaniline
- Diethyl ether dissociates when it reacts with
- NaOH
- H2O
- HI
- KMnO4
- Cresols are
- Hydroxy toluenes
- Dihydric phenols
- Trihydric phenols
- Trihydric alcohols
- IUPAC name of sec butyl alcohol is
- 1-butanol
- 2-butanol
- 2-methyl-1-butanol
- 2-methyl-2-butanol
- Methyl phenyl ether can be produced by reacting
- Phenolate ions and methyl iodide
- Bromobenzene with methoxide ions
- Methanol and phenol
- Bromobenzene and methyl iodide
- Ortho-nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and m-nitrophenol because
- Melting point of o-nitrophenol is lower than of m- and p- isomers
- O-nitrophenol is more volatile in steam than those of m- and p- isomers
- O-nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bonding
- O-nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bonding
- Primary alcohols can be prepared from alkenes by
- Mercuration and demercuration of alkene
- Direct hydration of alkenes
- Hydroboration of alkenes
- All of the above
- The reaction of alkoxide ion with alkyl halide to form ether is called
- Wurtz reaction
- Kolbe’s reaction
- Perkins reaction
- Williamsons synthesis
- In which case would a Williamson ether synthesis fail?
- Sodium ethoxide + iodomethane
- Sodium ethoxide + iodoethane
- Sodium ethoxide + 2-iodopropane
- Sodium ethoxide + 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
- Grain alcohol is the common name of
- Ethyl alcohol
- Amyl alcohol
- Methanol
- None of these
Answers (41-50)
41. (2)
2,4,6-Trinitrophenol
42. (3)


43. (1)
Cresols are hydroxy toluenes
44. (2)


2-butanol
45. (1)
Methyl phenyl ether (anisole) can be produced by reacting phenolate ions and methyl iodide.
46. (3)
Ortho-nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and m-nitrophenol because o-nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bonding.
47. (3)
Primary alcohols can be prepared from alkenes by hydroboration of alkenes.
48. (4)
Williamsons synthesis
49. (4)
2-iodo-2-methylpropane is a tertiary alcohol which will undergo dehydrohalogenation.
50. (1)
Grain alcohol is the common name of ethyl alcohol.
Assertion And Reasoning MCQs
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and but R is not a correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
1. Assertion (A) (CH3)3-CONa and CH3CH2Br react to form (CH3)3C-O-CH2CH3.
Reason (R) Good yields of ethers are obtained when teri-alkyl halides are treated with alkoxide.
2. Assertion (A) Ortho and para nitrophenols can be separated by steam distillation.
Reason (R) Ortho isomer associates through intermolecular hydrogen bonding while Para isomer associates through intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
3. Assertion (A) In Lucas test, 3° Alcohol react immediately.
Reason (R) An equimolar mixture of anhyd. ZnCI2 and conc. HCI is called Lucas reagent.
4. Assertion (A) The water solubility of the alcohols follow the order: tert-butyl alcohol > sec-butyl alcohol > n butyl alcohol .
Reason (R) Alcohols form H-bonding with water to show solution nature.
5. Assertion (A) Tert-butyl alcohol undergoes acid catalysed dehydration readily than propanol .
Reason (R) 3° Alcohol do not give Victor-Meyer’s test.
6. Assertion (A) Phenol is less acidic than p-nitrophenol.
Reason (R) Phenolate ion is more stable than p-nitrophenolate ion.
7. Assertion (A) Reimer-Tiemann reaction of phenol with CCI4 in NaOH at 340 K gives salicylic acid as the major product.
Reason (R) The reaction occurs through intermediate formation of dichlorocarbene.
8. Assertion (A) The C-O-C bond angle in ethers is slightly less than tetrahedral angle.
Reason (R) Due to the repulsive interaction between the two alkyl groups in ethers.
9. Assertion (A) Phenol undergo Kolbe reaction, ethanol does not.
Reason (R) Phenoxide ion is more basic than ethoxide ion.
10. Assertion (A) Etherates are coordination complexes of ethers with Lewis acids.
Reason (R) Ethers are easily cleaved by mineral acids such as HCI and H2SO4 at 373K.
11. Assertion (A) Boiling point of alcohols are higher than that of ethers of comparable molecular mass.
Reason (R) Alcohols can form intermolecular hydrogen bonding while ethers can not.
Assertion and Reasoning MCQ Answers
1. (c)
(CH3)3-CONa and CH3CH2Br react to form (CH3)3C-O-CH2CH3. Good yeild of ether are obtained when primary alkyl halides are treated with alkoxides derived from any alcohol.
2. (c)
Ortho and para iomers of nitro phenol can be separated be steam distillation because of nearby same boiling point of both and ortho ieomers associated by intramolecular hydrogen bonding and para isomers by hydrogen bonding.
3. (b)
In Lucas test, tertiary alcohols react immediately because of the formation of the more stable tertiary carbocation.
4. (b)
The tendency to show H-bonding decreases with increasing hydrophobic character of carbon chain. The hydrophobic character of carbon chain increases with the length of carbon chain.
5. (b)
Alcohols which form the most stable carbocations undergo dehydration more readily. Since tert-butyl alcohol forms more stable tert-butyl cation, therfore, it undergoes dehydration more readily than propanol.
6. (c)
p-Nitrophenolate ion is more stable than phenolate ion.
7. (c)
Nucleophilic attack of phenolate ion through the ortho-carbon atom occurs on CCl4 to form an intermediate which on hydrolysis gives salicylic acid.
8. (d)
In ethers, bond angle around oxygen has deviation caused due to repulsive interaction between bulkier alkyl groups.
9. (b)
On using tert-butyl bromide and sodium ethoxide as reactants, the major product would be 1-methylpropene and ethanol.
10. (c)
Ethers being Lewis bases form etherates with Lewis acids. Ethers are not easily cleaved by H2SO4.
11. (a)
Alcohols have high boiling point than ethers because intermolecular H-bonding is found in alcohols.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Why are ether more volatile than alcohols?
Ether does not form hydrogen bonds unlike alcohol, thus it is more volatile than alcohol.
Q2. Why diethyl ether can’t be used as an anesthetic?
Diethyl ether is a highly inflammable compound which makes it incompatible to be used as an anesthetic.
Click Below To Learn Chemistry Term-1 Syllabus Chapters MCQs
- Chapter-1: Solid State MCQ
- Chapter-2: Solution MCQ
- Chapter-7: P-Block Element MCQ
- Chapter 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQ
- Chapter 11: Alcohols Phenols and Ether MCQ
- Chapter-14: Biomolecules MCQ
Click Below To Learn Physics Term 1 Syllabus Chapter-Wise MCQs
Final Words
From the above article, you have practiced Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ of Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11. We hope that the above mentioned latest MCQs for Term 1 of Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers will surely help you in your exam.
If you have any doubts or queries regarding the Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Multiple Choice Questions with Answers of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry, feel free to reach us and we will get back to you as early as possible.
Click Below To Learn Physical Education Term-1 Syllabus Chapters MCQs
- Chapter 1: Planning in sports MCQ
- Chapter 2: Sports And Nutrition MCQ
- Chapter 5: Children and Women in Sports MCQ
- Chapter 6: Test and Measurement in Sports MCQ
- Chapter 8: Biomechanics and Sports MCQ