Last updated on July 24th, 2024 at 01:13 pm
Psychology In Sports
Definition & Importance of Psychology in Physical Education & Sports;
Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behavior of a sportsperson. It surrounds environmental factors that affect how people think, act, and feel. It also includes the study of conscious and unconscious situations.
Sports psychology: It is the branch of applied psychology that deals with sports performance and behavior of a player during training and competition.
It helps to modify a sportsperson according to the needs of the situation and optimize the benefits for better performance and excellence
Importance
- Psychology helps to improve the performance and personality of players by scientifically modifying their behavior.
- Proper motivation and feedback enhance the performance of the player.
- It helps to control and check the declining performance
- It helps to understand the learning rate, learning curve, development patterns, etc
- It develops proper behavior setup during the competition
- It helps the player deal with spectators and the crowd
- It helps to overcome the stress and tension of players It helps to understand the needs of a sportsperson
- It helps coaches make a better selection of players
- It improves the coaching, training and teaching skills for effective learning
Growth & Development
Growth
The term growth implies an increase in the size, height, length and weight of an individual. It is used in purely physical terms which implies quantitative changes, like the growth of arms, brain, Muscles, or the body in general.
Development
Development implies qualitative changes. It is changing in character leading to maturity of improvement in functioning. For example, arms grow large but also develop by undergoing certain changes that equip them for better work.
Differences Between Growth And Development
| Growth | Development |
|---|---|
| Growth implies changes in the size, length, height and weight of an individual. | Development implies overall changes in shape or form resulting in improved working or functioning. |
| Growth indicates the changes in the quantity | Development indicates the changes in quality |
| Growth is one of the aspects of the development process | Development is a wider term, which refers to overall changes in the individual |
| Growth does not continue throughout life | Development is a continuous process |
| The development indicates the changes in quality | Development describes the changes in the individual as a whole and does not list changes in parts |
| Growth may or may not bring development | Development is possible without growth |
| Growth is cellular and can be measured accurately | Development is functional or organizational |
Developmental Characteristics At Different Stages of Growth


Infancy Stage (Birth to 3 years)
During this stage, growth and development occur progressively. The child gains considerable weight and height. Cognitive development starts as the child tries to balance and to gain control over big muscles.
Childhood Stages ( 3 to 12 years)
Early Childhood Stage (3 to 6 years)
In this stage, the growth is slower. The child’s neuromuscular development and intellectual development is slow. Learning takes place through repetition and practice.
Children should participate in multiple activities. These activities should consist of easy and light exercises.
Middle Childhood Stage (7 to 10 years)
In this stage, children develop flexibility and coordination along with strength, and speed. Thus a lot of playful activities should be there in their curriculum like running, jumping, calisthenic exercises, and Yoga asanas.
Later Childhood Stage (11 to 12 years)
During this stage, growth is slower whereas development is very rapid. Muscles gain strength and neuromuscular coordination improves. Intellectual development comes through repetition, practice and experience. During this stage, children should participate in a lot of physical activities.
Adolescence Stage (13 to 19 years)
In this stage, the transition takes place from childhood to maturity. In this period, rapid development takes place physically, mentally, socially and emotionally.
During this stage, high-intensity activities are recommended for at least 60 minutes. They should involve themselves in muscle and bone-strengthening activities.
Adolescent Problems & Their Management
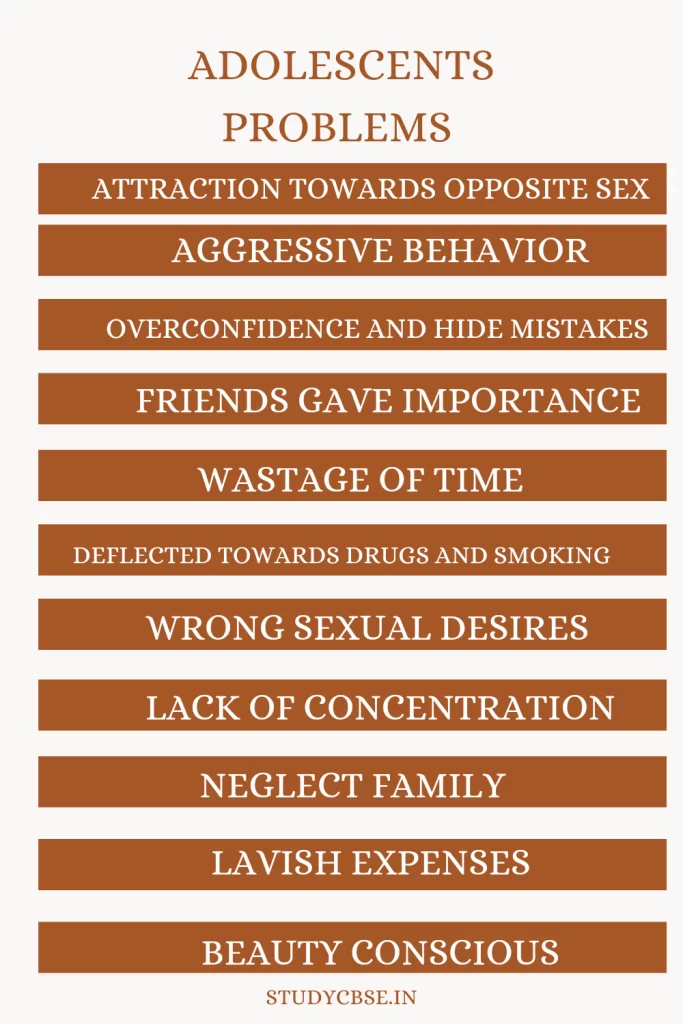

Aggressive Behavior: Adolescent has Aggressive behavior and often become violent very fast. They easily become irritated and repulsive
Overconfidence and hide mistakes: Teenagers are often overconfident and hide their mistakes and try to make fools of others.
Friends gave importance: Teenagers like the company of friends and enjoy being in a peer group.
Wastage of time: They often waste time on useless things like gossiping, talking, watching TV, listening to music, idle sitting, etc.
Deflected towards drugs and smoking: Often with the bad company of friends, they are deflected towards health hazards like smoking, drugs, alcohol, etc.
Wrong sexual desires: They sometimes commit wrong sexual relationships.
Lack of concentration: Teens have a low concentration on studies and many important works.
Neglect Family: They often neglect or avoid listening to their parents or teachers.
Lavish Expenses: They waste money on useless things like makeup, costly clothes, fast food, etc.
Beauty conscious: In this age, they are more conscious about the body, figure, beauty, etc.
Attraction towards the opposite sex: At this age, they are attracted to the opposite sex and have a lot of desire to interact with them
Inadequate rest and sleep: During this age, they have sleepless nights, and inadequate rest and sleep.
Management of Adolescence Problems
Providing a healthy atmosphere: The atmosphere at home and school should be healthy and cheerful for their proper growth and development.
Proper sex education: At this stage, adolescents must be properly guided to tackle sex problems and their doubts must be clear regarding sexual development.
Checking mistakes: At this stage, their faults and mistakes must be politely and sympathetically treated instead of punishing or blaming them.
Proper use of energy: Teenagers are very energetic, which needs to be channeled properly.
Mode of education: Education must be interestingly provided to them so that they explore their inner capabilities.
Development of moral values: At this stage, they must be properly taught about their cultures, traditions, and customs and follow them sincerely.
Team Cohesion and Sports
Great teams work like friends! They trust each other, help each other, and work together to win. Doing things together on and off the field makes them closer and stronger. Sports are awesome for learning and growing together.
Teams that celebrate wins and learn from mistakes get better and have more fun. Team spirit or team cohesion is about more than winning – it’s about making friends and learning important things like teamwork and how to be nice (empathy).
What we learn in sports helps us in life too! Coaches, players, and fans let’s all work together to make sports friendly and fun for everyone!
Introduction to Psychological Attributes: Attention, Resilience, Mental Toughness
In the realm of psychology, certain attributes play a significant role in shaping our behaviors, responses, and overall well-being. Three essential psychological attributes are attention, resilience, and mental toughness. Let’s briefly explore each of them:
Attention:
Attention is our ability to focus on specific stimuli or tasks while filtering out distractions. It’s like a spotlight that illuminates what matters most at any given moment.
Being attentive helps us absorb information effectively, make better decisions, and perform well in various areas of life. In today’s fast-paced world filled with distractions, nurturing and improving our attention is crucial for enhanced productivity and overall mental clarity.
Resilience:
Resilience is our ability to bounce back from adversity, challenges, or setbacks. Life can throw unexpected curveballs, and resilience enables us to cope with stress, adapt to changes, and maintain our emotional well-being.
Building resilience involves developing a positive mindset, cultivating support networks, and learning from experiences, turning difficulties into opportunities for growth and learning.
Mental Toughness:
Mental toughness refers to the mental and emotional strength that allows us to persevere and perform at our best, even under pressure or in the face of adversity. It involves maintaining focus, staying determined, and managing stress effectively.
Mental toughness is often seen in high-performing athletes, leaders, and individuals who push their limits to achieve their goals. Developing mental toughness involves consistent practice, self-belief, and the willingness to step outside our comfort zones.
Click Below To Learn Other Chapter Notes
- Class 11 Physical Education Syllabus
- Chapter 1: Changing Trend and Career Option
- Chapter 2: Olympic value education
- Chapter 3: Yoga
- Chapter 4: Physical Education and sports for CWSN
- Chapter 5: Physical Fitness, Wellness
- Chapter 6: Test Measurement And Evaluation
- Chapter 7: Fundamentals of Anatomy, Physiology In Sports
- Chapter 8: Fundamentals of Kinesiology and Biomechanics in Sports
- Chapter 9: Psychology in Sports
- Chapter 10: Training And Doping In Sports
Psychology in sports chapter 9 CBSE, class 11 Physical Education notes. This cbse Physical Education class 11 notes has a brief explanation of every topic that NCERT syllabus has.
You will also get ncert solutions, cbse class 11 Physical Education sample paper, cbse Physical Education class 11 previous year paper.
Final Words
From the above article you must have learnt about ncert cbse class 11 Physical Education notes of chapter 9 Psychology in sports. We hope that this crisp and latest Physical Education class 11 notes will definitely help you in your exam.